Explanation
KMS standard and exclusions
- Explanation of the documentation in the quality management system
1.1 Introduction
The documented quality management system (KMS) contains documents necessary to control the processes of the organization To let expire. The aim is to provide optimal quality of care, given the needs and expectations of our clients (and their legal representatives).
Through a good intake, evaluations of care and customer satisfaction survey, we determine what the needs and expectations of clients and determine whether we are meeting those needs and meet expectations. Based on our understanding of the needs and expectations of our clients, we have a number of quality features (aspects of our organization that are quality-critical) established. Examples of quality attributes are: the care matches the care demand and is effective, continuity of care, the care recipient is well involved, client safety. In document 2.2 Targets and quality policy these quality characteristics have been worked out.
In addition, there are various tools to to identify undesirable situations and to take measures to prevent recurrence to prevent it. For example, we have arrangements for handling complaints and incidents, we measure whether the goals are being achieved and we conduct internal audits out.
1.2 Documents from the KMS
The documents that are part of our KMS are process descriptions and working documents. These can be consulted in Zilliz, Intranet Titurel under the map Quality Manual. The quality manual is therefore available to all employees accessible.
1.3 Process descriptions
The processes are the heart of the KMS. Processes are
series of activities that are repeated regularly. As the most important
work processes are controlled, we control the service. Precisely because of
the repetitive nature of activities, it is possible to
build in evaluation moments and process indicators determine whether
processes run smoothly. Process descriptions provide for the control of
critical steps in the processes by indicating who is responsible
for which step, which working documents are available at which step and
which registrations arise from the activities. Because of the overview,
any detailed information provided through the working documents and not in the
process descriptions.
1.4 Working documents
Working documents describe details needed to to be able to properly carry out steps within processes. We strive to only develop working documents where they have added value.
1.5 Digital Handbook
The documents can only be consulted digitally via zilliz.
In the 1.3 Process Document management and registrations state how we take care for the control of documents and records.
1.6
Diagram coherence critical processes
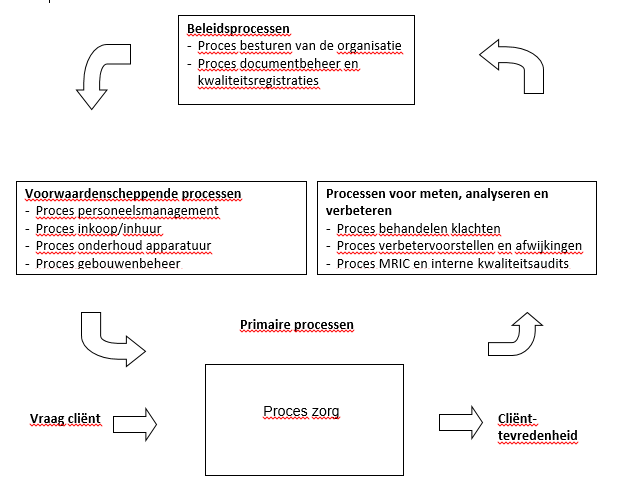
- Scope of the KMS (where did it refers to)
Titurel offers care to people with a disorder in the autistic spectrum, an intellectual disability and/or psychological problems.
- Normverwijzing
De Titurel has developed the KMS based on ISO for Care and welfare (ISO152240: 2015.
- Exclusions
The following paragraphs of the standard are excluded:
| No | Motive |
| 8.3 | Within the institution, there is no development of entirely new services place. |
| 8.5 | There are no physical third-party or customer products. |
| 9.1 | No use is made of monitoring- and/or measuring equipment. |
- Explanation of paragraph 4 'Quality management systems' in the norm
- The critical processes and their mutual coherence has been determined see section 1.6 of this explanation.
- The quality policy is described in the document 'Objectives and quality policy’.
- The subject and scope of the quality management system are described in paragraph 2 (Scope) of this document.
- The control of documentation and quality registrations is described in Process Document management and quality registrations.
- Explanation of paragraph 5 ‘Management responsibility’ in the standard
- The director/driver van Titurel performs as ‘management representative’ as referred to in paragraph 5.1 in this standard. The director/administrator has taken care of the development, introduction and the keep track of the system.
- It quality policy is described. Based on knowledge of the needs and expectations of the clients are the quality characteristics and associated measuring points determined and included in the document ‘Objectives and quality policy’. It does not contain the concrete objectives of the measuring points, because they can be changed every year. The objectives are in the annual plan.
- Responsibilities and powers of employees are in the process descriptions and in the job profiles.
- The internal communication is controlled; there is a consultation schedule established.
- Policy documents are issued during the monitored by those responsible for the document for a year and in addition, a system assessment carried out at least once a year in which the policy documents are evaluated.
- Explanation of paragraph 6 ‘Management of resources’ in the standard
- The employees are the most critical “resources” of the organization. Employees are selected based on job requirements. The competence of the employees is governed by the determining the competences (o.a. during performance reviews) and through schooling.
- The workspaces where clients come, are suitable for the service. The spaces are equipped with fire extinguishers and emergency exits. Evacuation drills are held periodically and evaluated.
- The automated system is provided of virus protection and passwords. Regular backups are made of critical data.
- Explanation of paragraph 7 'Realizing the product' in the standard
- The processes associated with clients are determined, defined and controlled. See the descriptions of the Process Care.
- The purchase of products and services (as far as critical for the service) is controlled in accordance with Process Purchasing.
- With regard to requirements regarding 'identification', the care provided is registered in the care files and the is it known which care provider provided care at what time.
- Care is taken with client property. Should client property be damaged due to the fault of staff, then in consultation with the client or his/her representative looked for a suitable solution.
- Explanation of paragraph 8 'Measurement, analysis and improvement' in the standard
- Periodically, the client satisfaction determined.
- Internal audits held in accordance with the Process Internal quality audits.
- For the critical processes, objectives have been determined and recorded in the annual plan. It course of the processes and the achievement of the objectives is monitored.
- The care becomes monitored through setting care goals and evaluating those goals.
- Differences (as care that has not been delivered as agreed, complaints and incidents) turn into registered in the MRIC overview and the improvement matrix. Corrective measures are determined to correct the deviations and to prevent recurrence to prevent it. Preventive measures are determined to prevent the occurrence prevent deviations. In the improvement matrix, the settlements of notifications tracked.



